Abstract
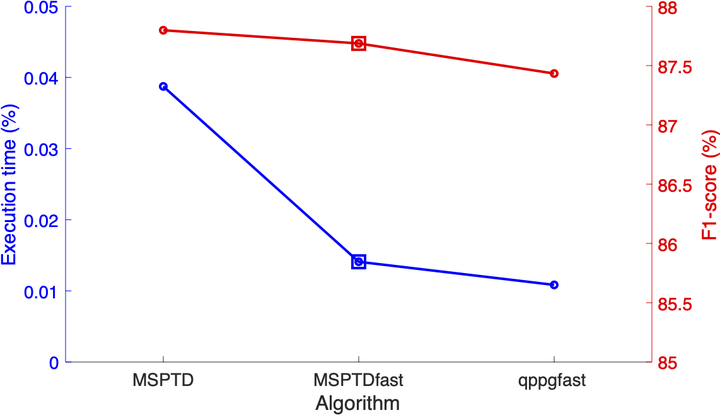
Introduction: Beat detection is a key step in the analysis of photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals. The MSPTD algorithm was recently identified as one of the most accurate beat detection algorithms, but its current open-source implementation is substantially more computationally expensive than other leading algorithms such as qppgfast. The aim of this work was to develop a more efficient, open-source implementation of the MSPTD algorithm. Methods: Five potential improvements were identified to increase efficiency. Each potential improvement was evaluated in turn, and an optimal algorithm configuration named MSPTDfast was developed which incorporated all of the improvements found to reduce algorithm execution time whilst not substantially reducing the accuracy of beat detection. Performance was assessed using data collected from young adults during a lunchbreak in the PPG-DaLiA dataset. The data consisted of wrist PPG signals acquired using an Empatica E4 device, alongside simultaneous ECG signals from which reference heartbeat timings were obtained. Results: MSPTDfast was found to be substantially more efficient than MSPTD (a reduction in execution time of 72.3%), with minimal difference in beat detection accuracy (F1-score 87.8% vs. 87.7%). In addition, the performance of MSPTDfast was much closer to that of the state-of-the-art qppgfast algorithm than the MSPTD algorithm, with a comparable F1-score (87.4% vs. 87.7%), and an execution time which was only 19.2% longer than that of qppgfast (vs. 330.8% longer for MSPTD). Conclusion: In conclusion, MSPTDfast is an efficient and accurate open-source PPG beat detection algorithm with a substantially faster execution time than MSPTD. It is available under the permissive MIT licence.
Accompanying presentation
The presentation which accompanies this paper is available here.