A new framework to estimate breathing rate from electrocardiogram, photoplethysmogram, and blood pressure signals
 Source: A. Adami et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Source: A. Adami et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Abstract
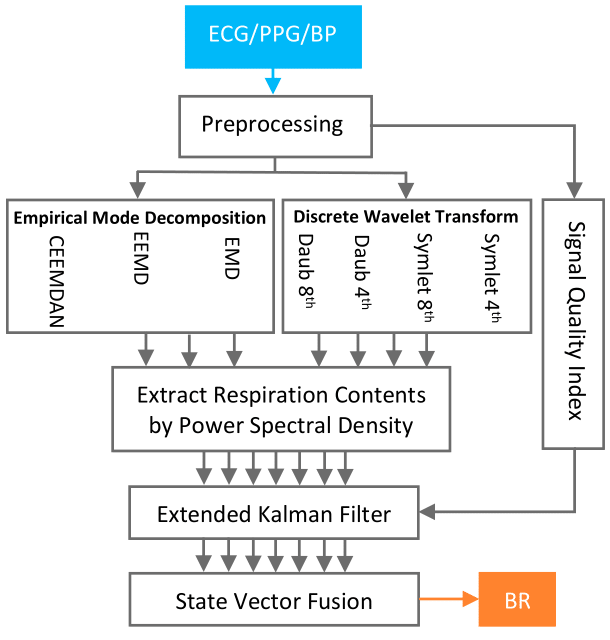
Breathing Rate (BR) is a key physiological parameter measured in a wide range of clinical settings. However, it is still widely measured manually. In this paper, a novel framework is proposed to estimate the BR from an electrocardiogram (ECG), a photoplethysmogram (PPG), or a blood pressure (BP) signal. The framework uses Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) methods to extract respiratory signals, taking advantage of both time and frequency domain information. An Extended Kalman Filter (EKF), incorporating a Signal Quality Index (SQI), enabled our method to achieve acceptable performance even for significantly distorted periods of the signals. Using state vector fusion, the output signals are combined and finally the BR is estimated. The framework was tested on two publicly available clinical databases: the MIT-BIH Polysomnographic and BIDMC databases. Performance was evaluated using the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). The results indicated high accuracy: MAPEs on the two databases of 3.9% and 3.6% for ECG signals, 6.0% for PPG, and 5.0% for BP signals. The results also indicated high robustness to noise down to 0dB. Therefore, this framework may have utility for BR monitoring in high noise settings.