 Source P.H. Charlton (CC BY 4.0)
Source P.H. Charlton (CC BY 4.0)
Overview
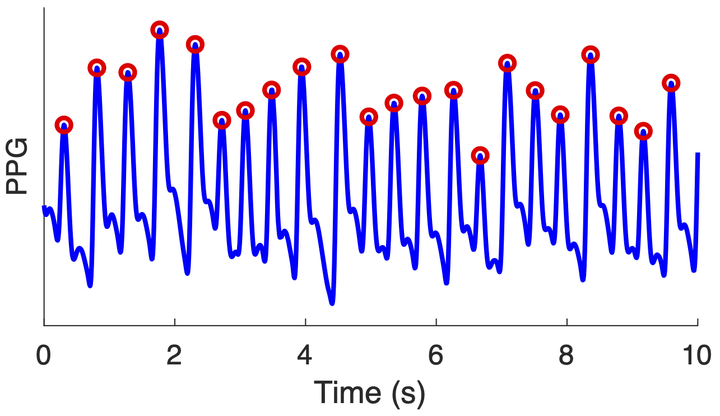
The aim of this project is to develop a high-performance algorithm to detect heartbeats in photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals - the signals measured by smartwatches and pulse oximeters.
Background
Smart wearables such as smartwatches and wrist-worn fitness trackers use photoplethysmography to monitor heart rate and rhythm. They do so by using an optical sensor to measure the photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal, and then analysing this signal to obtain heart rate or rhythm. A key step in analysing the signal is to identify individual heartbeats in the signal. Several approaches have previously been proposed to identify heartbeats in the signal, although it is not yet clear how well they perform, and whether they perform sufficiently well for clinical use.
Aim
The aim of this project is to identify, or develop, a high-performance algorithm to detect heartbeats in photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals.
Methods
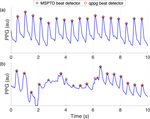
The performance of existing PPG beat detection algorithms was assessed in different use cases, when using the algorithms with clinical monitoring data, and also wearable data. In addition, the impact of patient demographics and physiology was also assessed.
Results
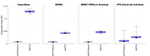
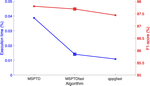
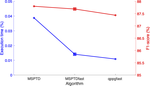
The results are available in detail in this publication. They are summarised in the following leaderboards:
Resources
The study is accompanied by the following resources, which are being made available here:
- PPG Beat Detection Algorithms: A selection of open-source algorithms for detecting beats in PPG signals.
- Performance Assessment Resources: Resources to assess the performance of PPG beat detectors, including:
- Tutorials on how to use the algorithms, datasets, and code.